One of the most important issues in most major cities of Iran is the provision of water in emergency situation caused by destructive earthquakes. For example, under normal conditions in Tehran, the city’s water supply is carried out by a system consisting of main water distribution pipelines from five reservoir dams (Amir Kabir, Letian, Lar, Taleghan and Mamlou) and water harvesting wells from Tehran plain aquifer along with water treatment plants and water distribution network throughout the city with an area of approximately 700 square kilometers and a population of 8.6 million people. Construction of this system has begun since the beginning of the 1960s in Tehran and has gradually developed with the expansion of Tehran and its population. Under normal circumstances, the management of this network has its own points and complexities (dynamic issues such as water quality management in resources and distribution network, providing the necessary water pressure, consumption and demand management, unaccompanied water management, passive defense, etc.).
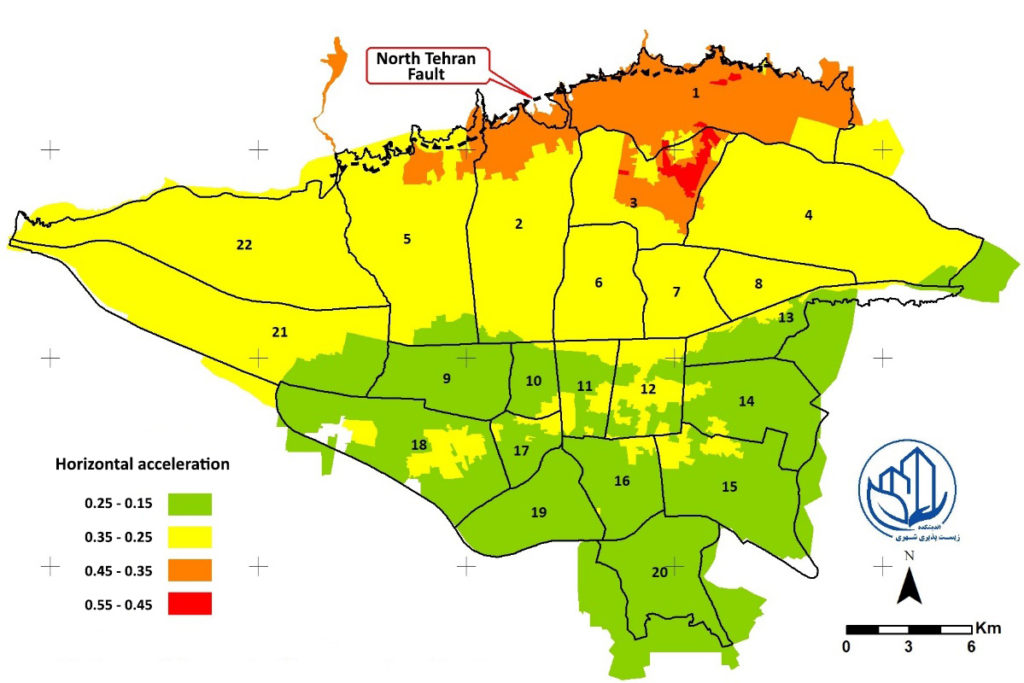
However, in an emergency situation caused by the earthquake in Tehran, the system will be out of orbit for several reasons. The emergencies caused by the earthquake in Tehran are the issue of activation of one of the main faults such as the north-Tehran routing fault, which is capable of causing an earthquake as big as 7 Richter. In the above figure, you can see the simulation of the seismic behavior of the city as a result of the activation of the mentioned fault. As can be seen, the whole district 1 and parts of districts 2, 3 and 5 of Tehran will face an acceleration of more than 0.35 g. Therefore, the probability of extensive damage in these parts is high. This damage can include the destruction of residential, administrative, service and commercial buildings as well as urban infrastructure such as the city’s water supply and distribution system. The city of Tehran will have complicated issues ahead under these circumstances. One of these problems will be solving the problem of providing sanitary water and firefighting from the first day after the incident to a year later. In order to solve this problem, all aspects of this complex and multidimensional problem must be carefully identified. A problem that is faced with the social behavior of citizens in the shock conditions caused by the earthquake and its consequences, a problem that is faced with the unavailability of the whole or part of the water supply and distribution system that mentioned in the previous paragraph, On the other hand, there is a need for sanitary water from the hours after the earthquake and the possibility of widespread fire fronts in many places of the city, witch there is no more efficient method arranged to extinguishing it than water. Conditions that are more complicated by the possibility of unavailability of Tehran’s technicians and water experts (in the form of the possible consequences of the earthquake) and the need for extensive team cooperation of citizens in unusual situations also call into question the realization of common measures.
Therefore, this team will be formed in the form of one of the subgroups of “Urban Water Restoration Scientific-Research Group” to start a multi-specific team activity by investigating the problem and trying to identify it. Members of this team, while familiarizing themselves with one of the faces of urban water issues, will practice the skills of diagnosis, explanation and analysis of the problem. Of course, problem solving will not be one of the expected goals of this team, this activity will be hand-hanging to familiarize with the land and place of living, capacity building in team behavior and multi-disciplinary and accepting the role of problem solver as one of the good experts of the future of the country. Activities that can be placed on the teamwork agenda in the form of this group will be as follows:
- Familiarity with the current status of Tehran’s water supply system (distribution network and water resources)
- Familiarity with water resources in Tehran
- Familiarity with water resources in Tehran
- Familiarity with the scenarios of Tehran’s situation against earthquake
- Trying to explain and identify the status of Tehran’s water supply system in earthquake conditions
- Efforts to explain and identify the social behavior of citizens of Tehran in the event of an earthquake
- Familiarity with the experiences or measures of emergency water supply in earthquake situations
In addition to office exercises, the above-mentioned process will benefit from a series of field observations to increase the productivity of activities. The list of these field observations will be programmable and performed as follows:
- Visiting water treatment plants in Tehran
- Visiting emergency water reservoirs in Tehran (which are built as a sample or under construction)
- Visiting the Tehran earthquake warning online system
- Visiting the north Tehran fault